
Das TE417-Modul unterstützt Micro SD-Karten, Micro SDHC-Karten (High Speed), Micro SD(<=2G) und Micro SDHC(<=32G). Die Stromversorgung ist bei 4,5V - 5,5V.
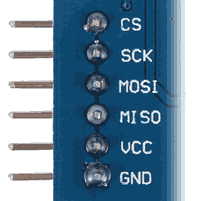
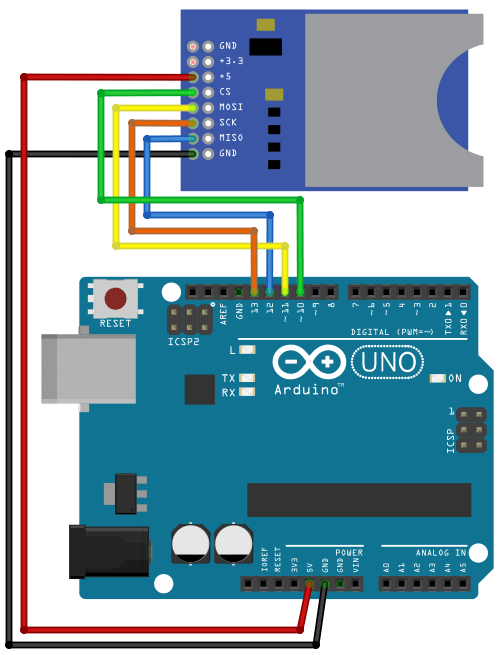
Das TE417-Modul verfügt über eine SPI-Schnittstelle, die mit dem Arduino folgendermaßen verbunden werden muss:
| Arduino | TE417 |
|---|---|
| 5V | VCC |
| GND | GND |
| beliebiger, freier digitaler Pin | CS (Chip Select) |
| 13 | SCK (Serial Clock) |
| 11 | MOSI (Master Out Slave In) |
| 12 | MISO (Master In Slave Out) |
Für detailliertere Informationen über das SPI-Protokoll in Verbindung mit dem Arduino sind folgende Links interessant:
- Introduction to SPI: https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/SPI
- Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI): https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/serial-peripheral-interface-spi
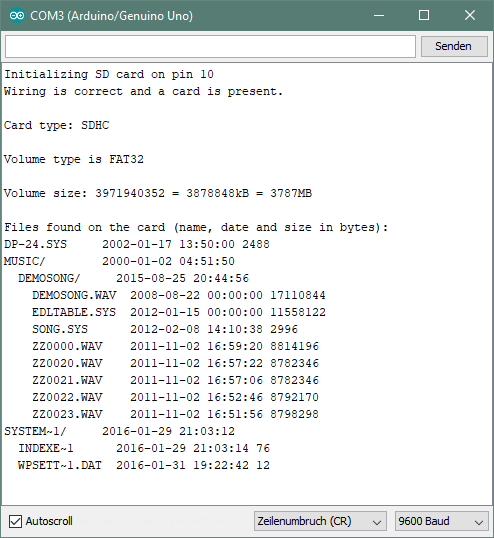
Eine beliebige SD-Karte wird in das Modul eingelegt (idealerweise mit einige vorhandenen Daten) und der erste Sketch "sd_card_test" wird auf dem Arduino ausgeführt. In der seriellen Konsole erscheint eine ähnliche Ausgabe wie folgt:
#define PIN_CS 10
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
Sd2Card card;
SdVolume volume;
SdFile root;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for serial port to connect.
}
Serial.print("Initializing SD card on pin " + String(PIN_CS) + "...");
if (!card.init(SPI_HALF_SPEED, PIN_CS)) {
Serial.println("Initialization failed. Things to check:");
Serial.println("- SD card inserted?");
Serial.println("- Is your wiring correct?");
Serial.println("- Did you change the chipSelect pin to match the module?");
return;
} else {
Serial.println("Wiring is correct and a card is present.");
}
Serial.print("\nCard type: ");
switch (card.type()) {
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SD1:
Serial.println("SD1");
break;
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SD2:
Serial.println("SD2");
break;
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SDHC:
Serial.println("SDHC");
break;
default:
Serial.println("Unknown card type");
}
// Try to open the volume/partition - it should be FAT16 or FAT32
if (!volume.init(card)) {
Serial.println("Could not find FAT16/FAT32 partition.\nMake sure you've formatted the card");
return;
}
// Print type and size of the first FAT-type volume
uint32_t volumesize;
Serial.print("\nVolume type is FAT");
Serial.println(volume.fatType(), DEC);
Serial.println();
volumesize = volume.blocksPerCluster(); // clusters are collections of blocks
volumesize *= volume.clusterCount(); // we'll have a lot of clusters
volumesize *= 512; // SD card blocks are always 512 bytes
Serial.print("Volume size: ");
Serial.print(volumesize);
Serial.print(" = ");
volumesize /= 1024;
Serial.print(volumesize);
Serial.print("kB");
Serial.print(" = ");
volumesize /= 1024;
Serial.print(volumesize);
Serial.println("MB");
Serial.println("\nFiles found on the card (name, date and size in bytes): ");
root.openRoot(volume);
// list all files in the card with date and size
root.ls(LS_R | LS_DATE | LS_SIZE);
}
void loop()
{
}Zunächst muss die Datei "data.csv" auf die SD-Karte geladen werden, bevor diese in das TE417-Modul eingelegt wird. Nach dem Hochladen und Ausführen des Sketches erscheint in der seriellen Konsole folgende Ausgabe:
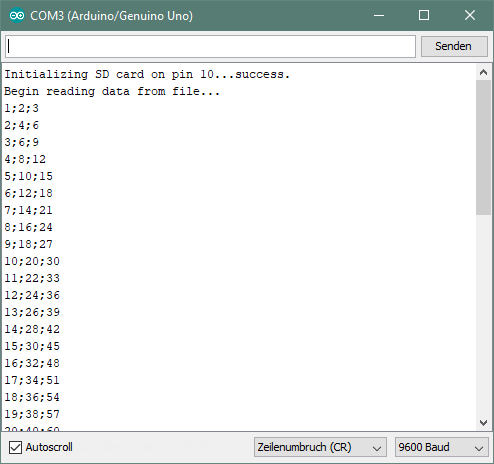
#define PIN_CS 10
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
File myFile;
const char *SD_FILE = "data.csv";
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.flush();
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for serial port to connect.
}
Serial.print("Initializing SD card on pin " + String(PIN_CS) + "...");
if (!SD.begin(PIN_CS)) {
Serial.println("failed!");
return;
}
Serial.println("success.");
Serial.println("Begin reading data from file...");
char* dataLine = "";
myFile = SD.open(SD_FILE, FILE_READ);
if (myFile) {
while(readLine(myFile, dataLine, 1024)) {
Serial.println(dataLine);
delay(50);
}
myFile.close();
} else {
Serial.println("File " + String(SD_FILE) + " not found!");
}
}
void loop()
{
}
bool readLine(File &inputFile, char* line, size_t maxLen) {
for (size_t n = 0; n < maxLen; n++) {
int c = inputFile.read();
if (c < 0 && n == 0) {
return false; // EOF
}
if (c < 0 || c == '\n') {
line[n] = 0;
return true;
}
line[n] = c;
}
return false;
}Im letzten Experiment wird nach dem Hochladen des Sketches zunächst eine neue Datei auf der Hauptebene der SD-Karte angelegt, in welche darauf einige Daten geschrieben werden. Anschließend wird die Datei wieder gelöscht.
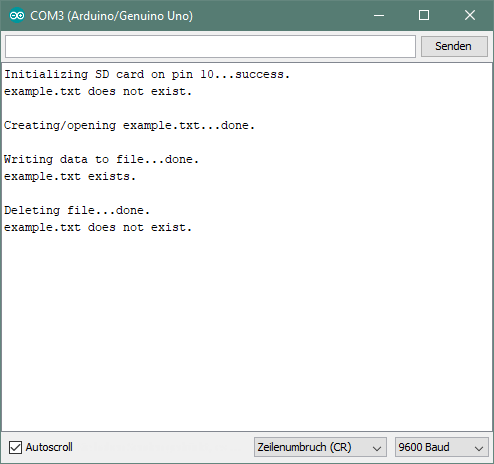
#define PIN_CS 10
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
File myFile;
const char *SD_FILE = "example.txt";
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.flush();
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for serial port to connect.
}
Serial.print("Initializing SD card on pin " + String(PIN_CS) + "...");
if (!SD.begin(PIN_CS)) {
Serial.println("failed!");
return;
}
Serial.println("success.");
printFileExist();
// open a new file and immediately close it:
Serial.print("\nCreating/opening " + String(SD_FILE) + "...");
myFile = SD.open(SD_FILE, FILE_WRITE);
Serial.println("done.");
Serial.print("\nWriting data to file...");
if (myFile) {
int pinValue;
for (byte i=0; i<20; i++) {
// get some random demo data from Pin1
pinValue = analogRead(1);
// write demo data to the file on the SD card
myFile.println(String(millis()) + "," + String(pinValue));
myFile.close();
}
}
Serial.println("done.");
printFileExist();
Serial.print("\nDeleting file...");
SD.remove(SD_FILE);
Serial.println("done.");
printFileExist();
}
void loop()
{
}
void printFileExist()
{
if (SD.exists(SD_FILE)) {
Serial.println(String(SD_FILE) + " exists.");
} else {
Serial.println(String(SD_FILE) + " does not exist.");
}
}