
Das folgende Joystick-Modul (oder auch Joypad-Modul) ist eine gute Eingabe-Möglichkeit für den Arduino, wenn es um zweidimensionale Koordinaten geht. Optional gibt es auch noch einen Knopf, der gedrückt werden kann (also ein digitales Signal).

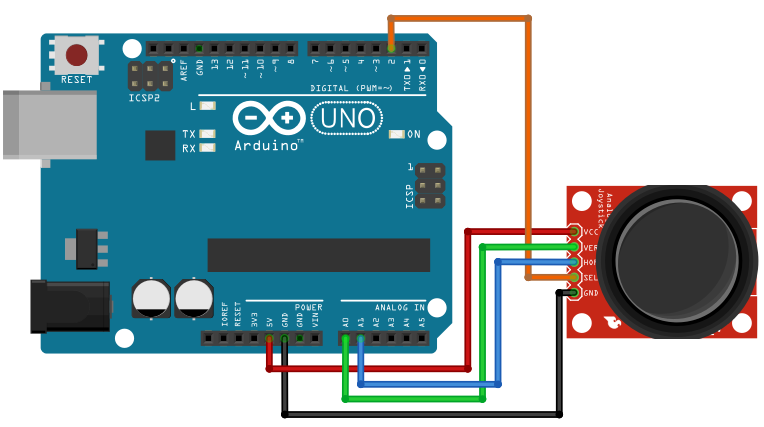
Der folgende Sketch gibt alle Änderungen in X- und Y-Richtung aus, sowie das Drücken des Joystick-Knopfes:
#define PIN_X A0
#define PIN_Y A1
#define PIN_BUTTON 2
const int tolerance = 10;
int xPos, xPosOld, yPos, yPosOld;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(PIN_X, INPUT);
pinMode(PIN_Y, INPUT);
// activate pull-up resistor on the push-button pin
pinMode(PIN_BUTTON, INPUT_PULLUP);
xPos = 0;
xPosOld = 0;
yPos = 0;
yPosOld = 0;
}
void loop()
{
xPos = analogRead(PIN_X);
yPos = analogRead(PIN_Y);
if (abs(xPos - xPosOld) > tolerance) {
Serial.print("X: ");
Serial.println(xPos);
xPosOld = xPos;
}
if (abs(yPos - yPosOld) > tolerance) {
Serial.print("Y: ");
Serial.println(yPos);
yPosOld = yPos;
}
if (digitalRead(PIN_BUTTON) == LOW) {
Serial.println("Button pressed!");
}
}